Gemini (Mithun)
Gemini, resembles the shape of twins when stars in this constellation are imaginarily connected, as per Indian mythology!
Where should I see…Orion and Taurus are the constellations towards west of Gemini constellation. If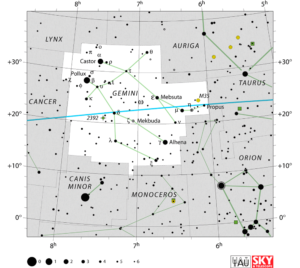 you move your eyes towards east, you will see another constellation named Cancer. In the North of Gemini, you will find Lynx and Auriga and in South, Canis Minor and Monoceros constellations. Gemini is halfway between celestial equator and North Pole, and so is fully part of Northern Hemisphere.
you move your eyes towards east, you will see another constellation named Cancer. In the North of Gemini, you will find Lynx and Auriga and in South, Canis Minor and Monoceros constellations. Gemini is halfway between celestial equator and North Pole, and so is fully part of Northern Hemisphere.
It covers up 514 square degree area of the sky. Area wise it is 30th largest constellation in the sky.
When and What can I see…It is on the zodiacal belt and hence is the 3rd zodiac on the zodiac belt. Sun enters in this constellation from 20th May to 21st June. It is best observed during September to May, as seen from India.
this constellation from 20th May to 21st June. It is best observed during September to May, as seen from India.
All you need is your naked eyes other than clear skies to see 123 stars of this constellations, as they are the one which are brighter than the lower limit of our naked eyes (i.e. 6.5 apparent magnitude) to see faintest stars.. The brightest star of this constellation is Castor. The Hindu name is Punarvasu.
Constellations are made up of single, binary (apparent and absolute), multiple and variable stars. Out of total 123 stars of different types, here is the list of 20 brightest stars as per their nature:
| Binary / Multiple Star system | Variable Stars | Binary and Variable Stars | Single stars |
| Alhena | Alzirr | Pollux | 1 |
| Wasat | – | Castor | – |
| 5 | – | Tejat | – |
| – | – | Mebsuta | – |
| – | – | Propus | – |
| – | – | Mekbuda | – |
| – | – | 6 | – |
| 7 | 1 | 11 | 1 |
As per Hindi mythology, there are no such known stories for this constellation.
Deep Sky Objects…
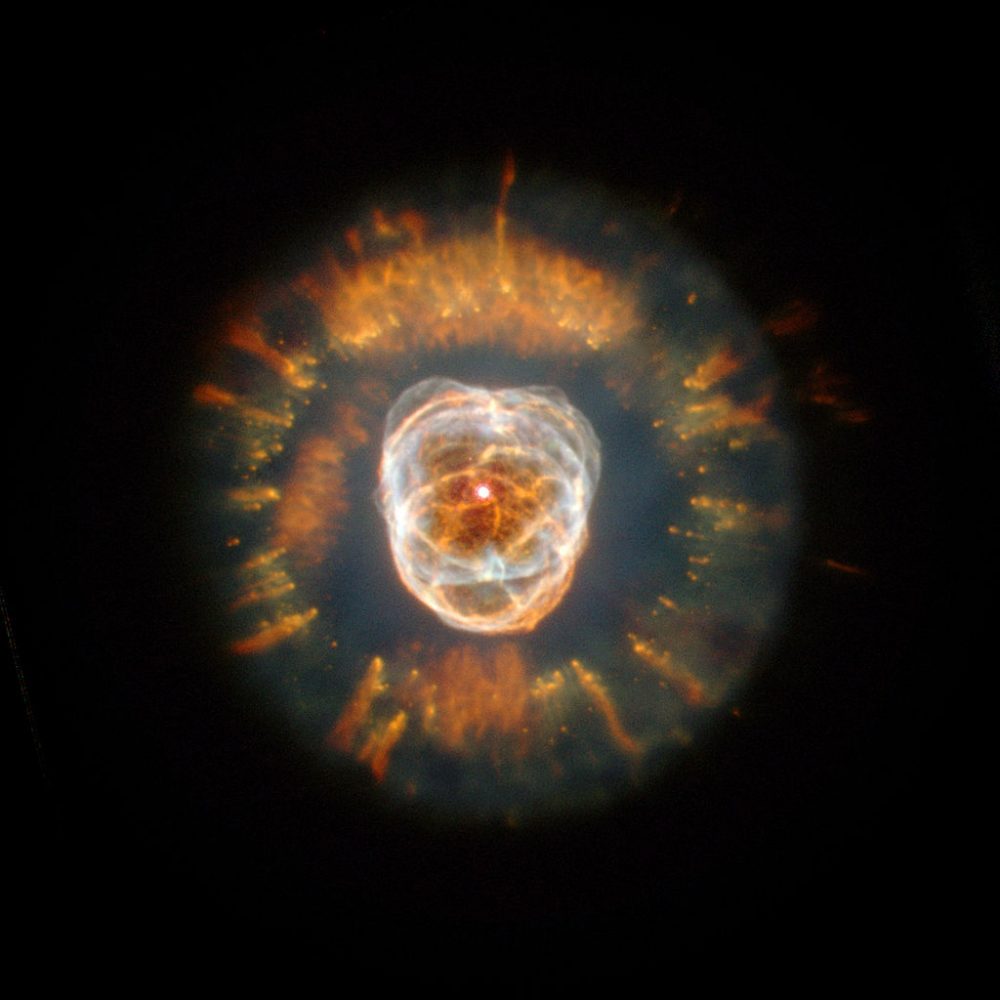 Eskimo Nebula or NGC 2392 || Bipolar Double Shell Planetary Nebula
Eskimo Nebula or NGC 2392 || Bipolar Double Shell Planetary Nebula
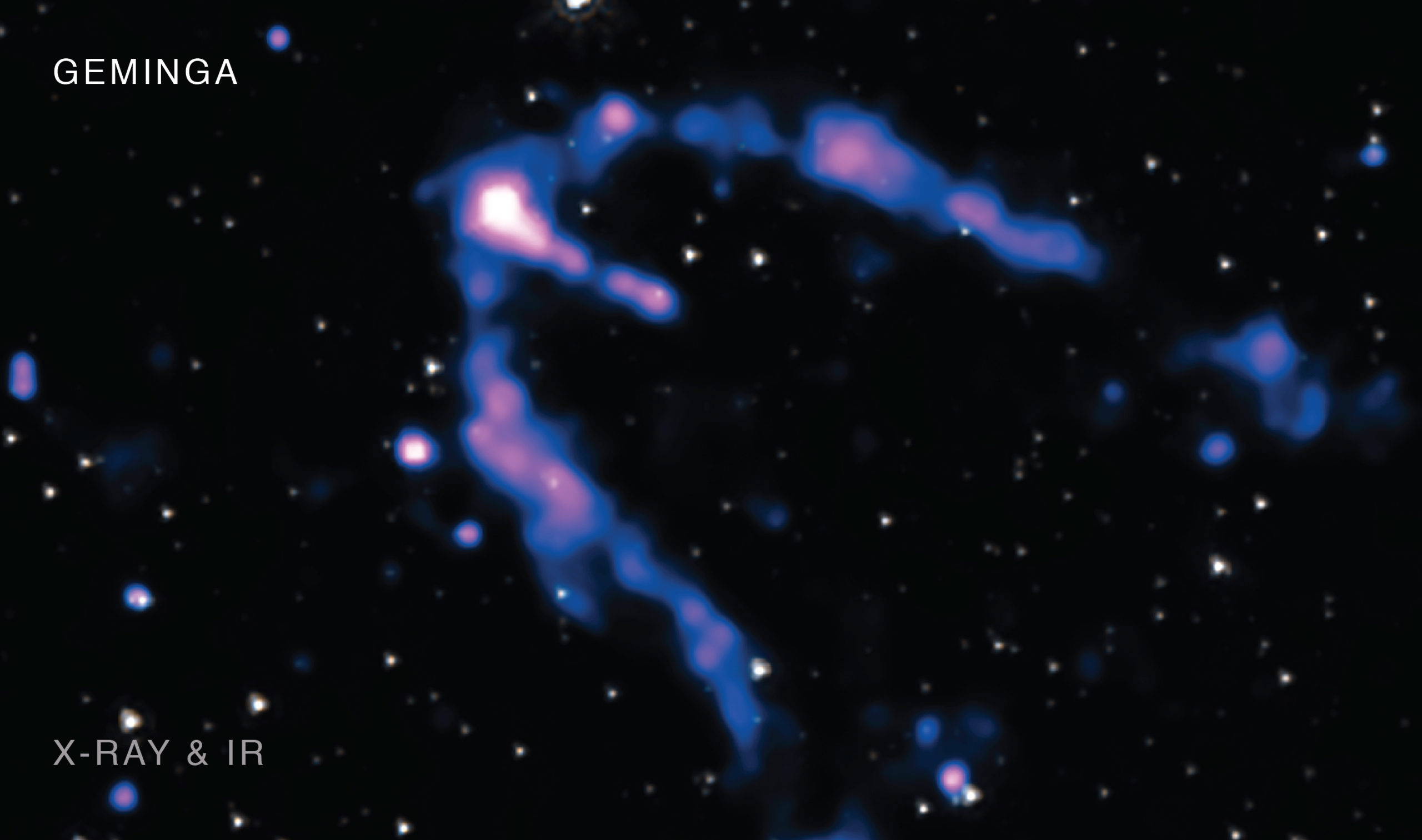 Geminga || Neutron Star
Geminga || Neutron Star
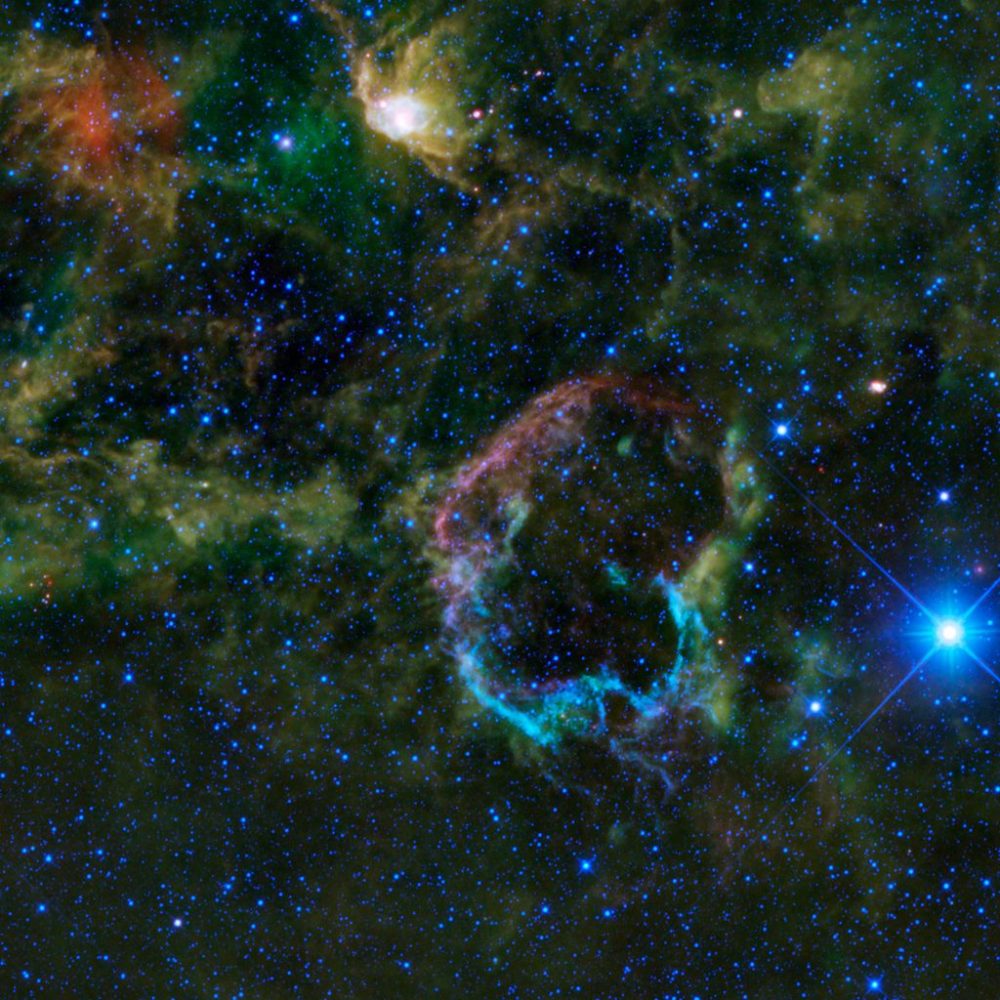 Jellyfish Nebula or IC 443 || Supernova Remanant
Jellyfish Nebula or IC 443 || Supernova RemanantAll the stars that we see naked eyes, all belong to our own, Milky way galaxy (Akash Ganga Tara Vishv). Bright stars can be seen naked eye and faint one through telescope. But the curtain of sky that we see in 2D is actually a huge universe we are talking about, with 3 dimension. There are many nebulous objects visible in every constellations. They differ widely by distances and nature. Like Emission Nebula, Reflecting Nebula, Absorption Nebula, Star Birth Nebula, Supernova Remnants (SNR) and Open Stars cluster which are within the disk of our own Milky Way galaxy. Globular cluster are also found, which are in the halo of our galaxy and some most distant objects like galaxies are also visible through telescope. Such objects are defined as “Deep Sky Objects”.
In this constellation there are 106 such different types of Deep Sky Objects observed. Below is the list of 20 brightest Deep Sky Objects:
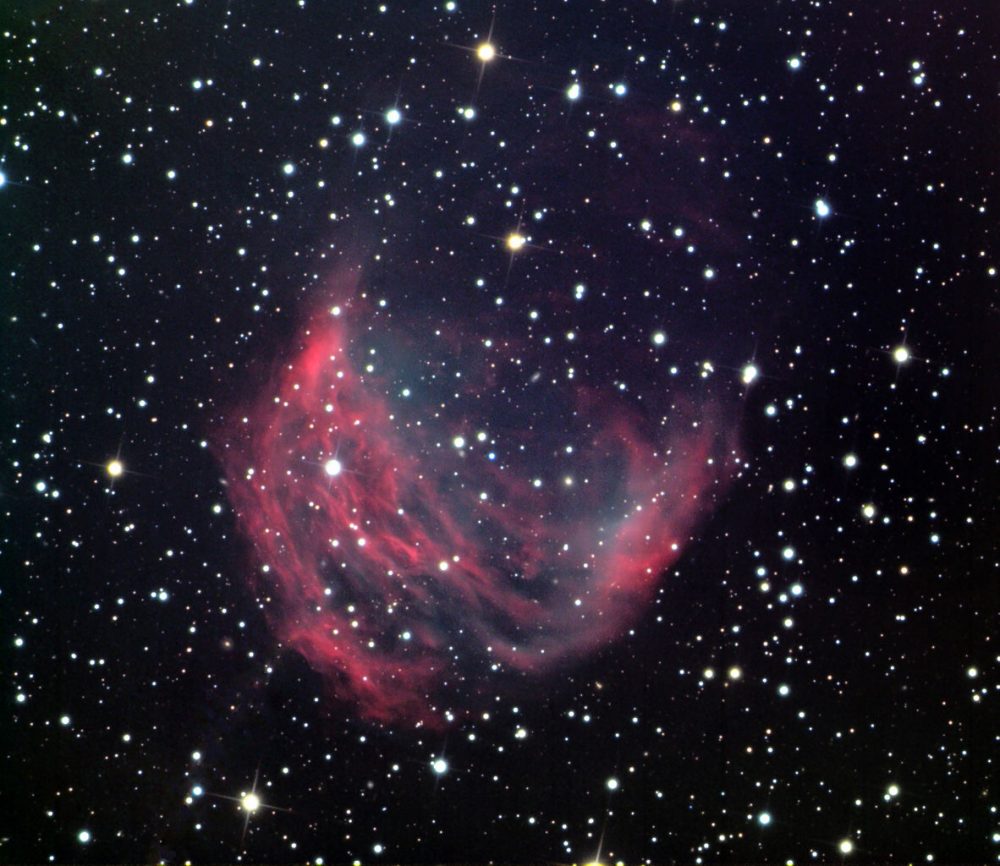 Medusa Nebula || Planetary Nebula
Medusa Nebula || Planetary Nebula
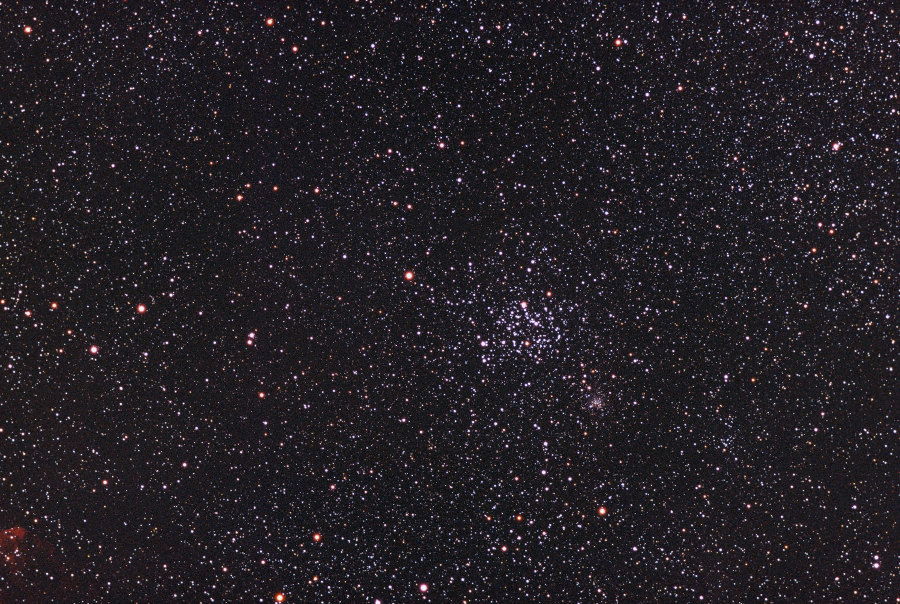 M35 or NGC 2168 || Open Cluster
M35 or NGC 2168 || Open Cluster
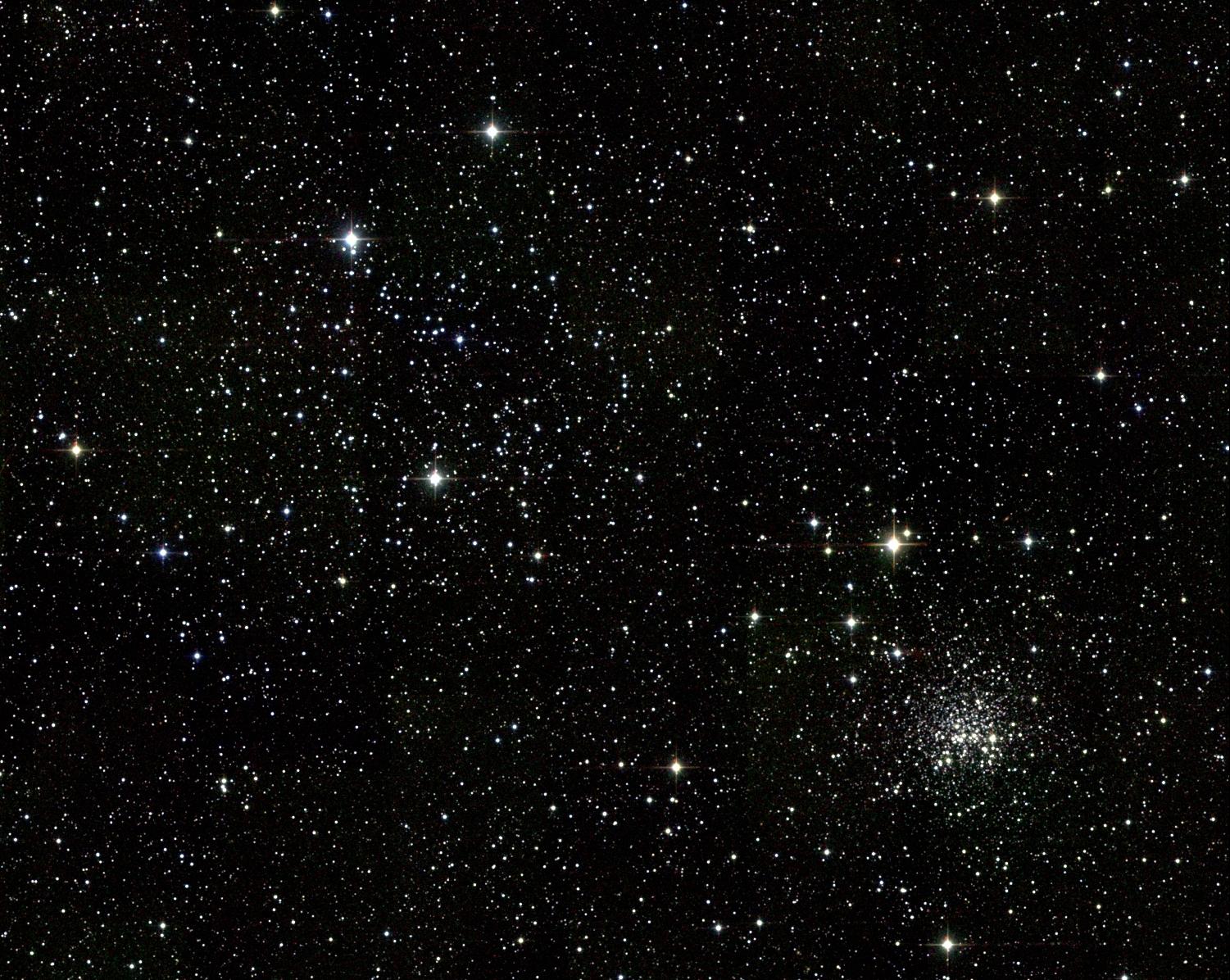 NGC 2158 || Open Cluster
NGC 2158 || Open Cluster| Galaxy | Open Cluster | Globular Cluster | Nebula | Supernova Remnant | ||
| Naked eye visibility | – | M35 | – | – | – | |
| Visible through Telescope | 6 | 9 | – | 3 | 1 | |
| 6 | 10 | – | 3 | 1 |
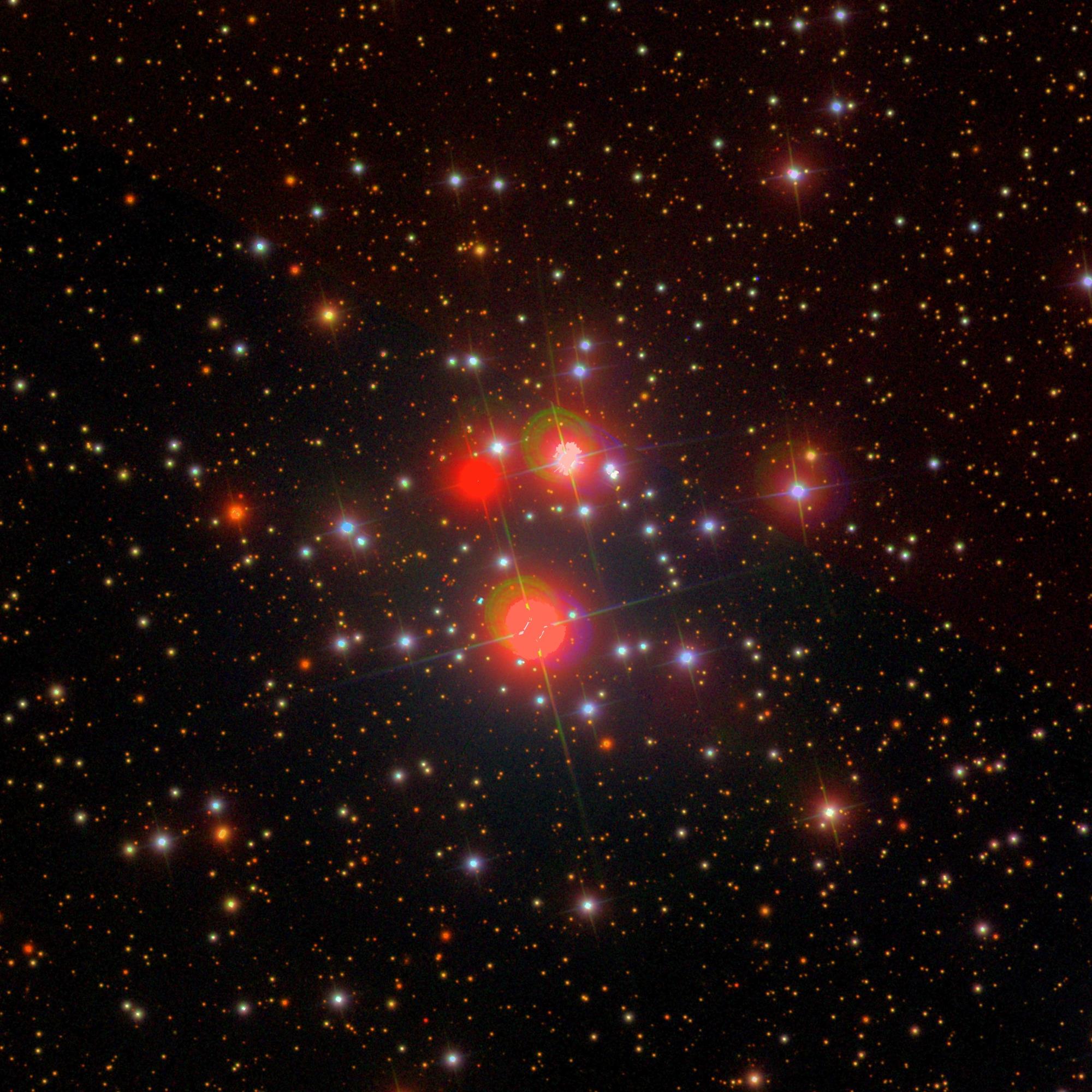 NGC 2129 || Open Cluster
NGC 2129 || Open Cluster
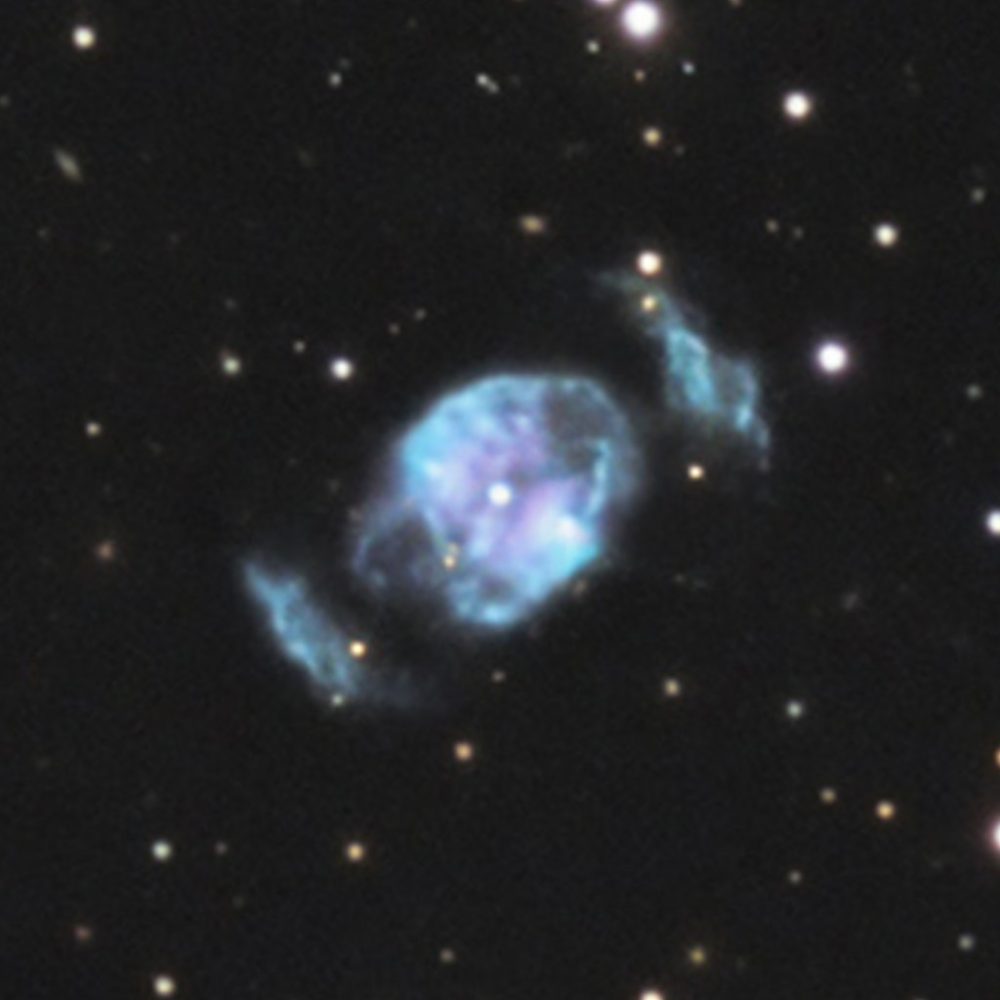 NGC 2371 || Dual Lobed Planetary Nebula
NGC 2371 || Dual Lobed Planetary Nebula
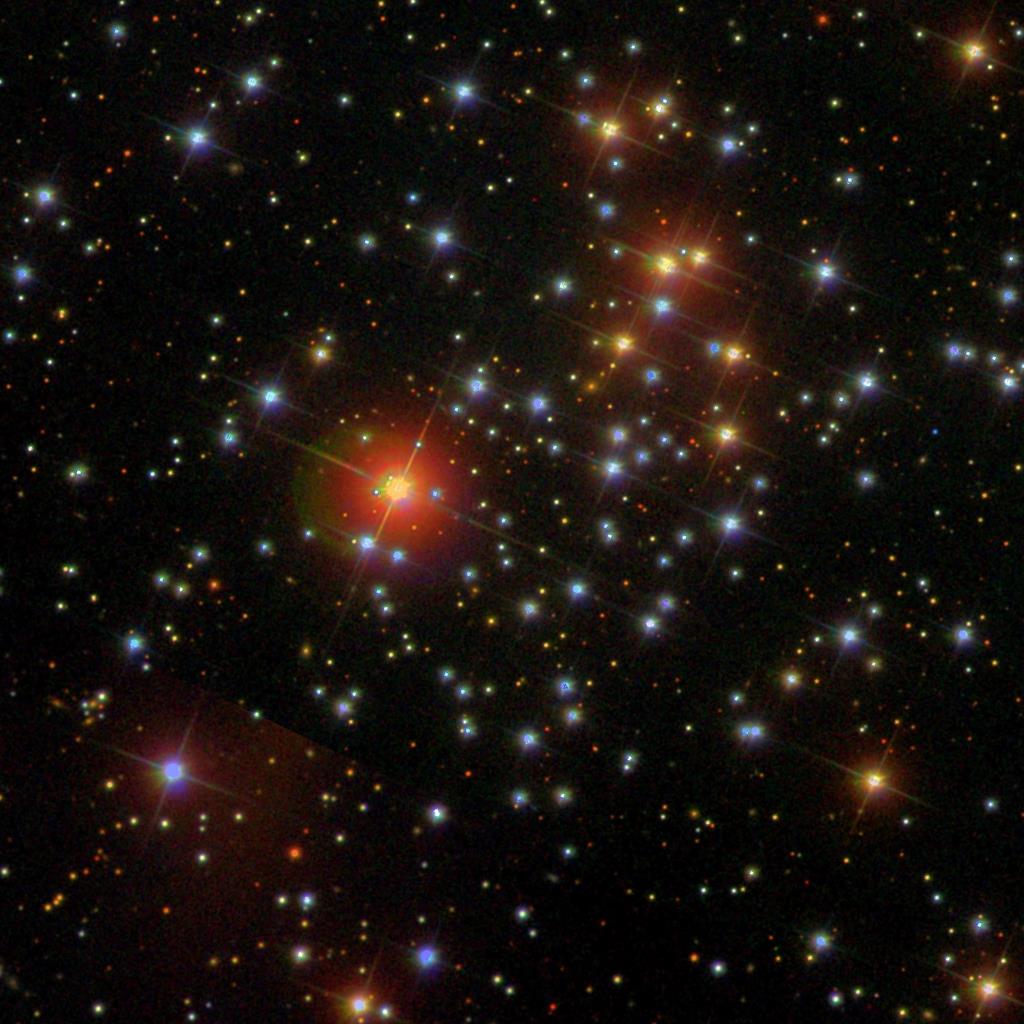 NGC 2355 || Open Cluster
NGC 2355 || Open Cluster

